2nd Type of Diabetes & Symptoms
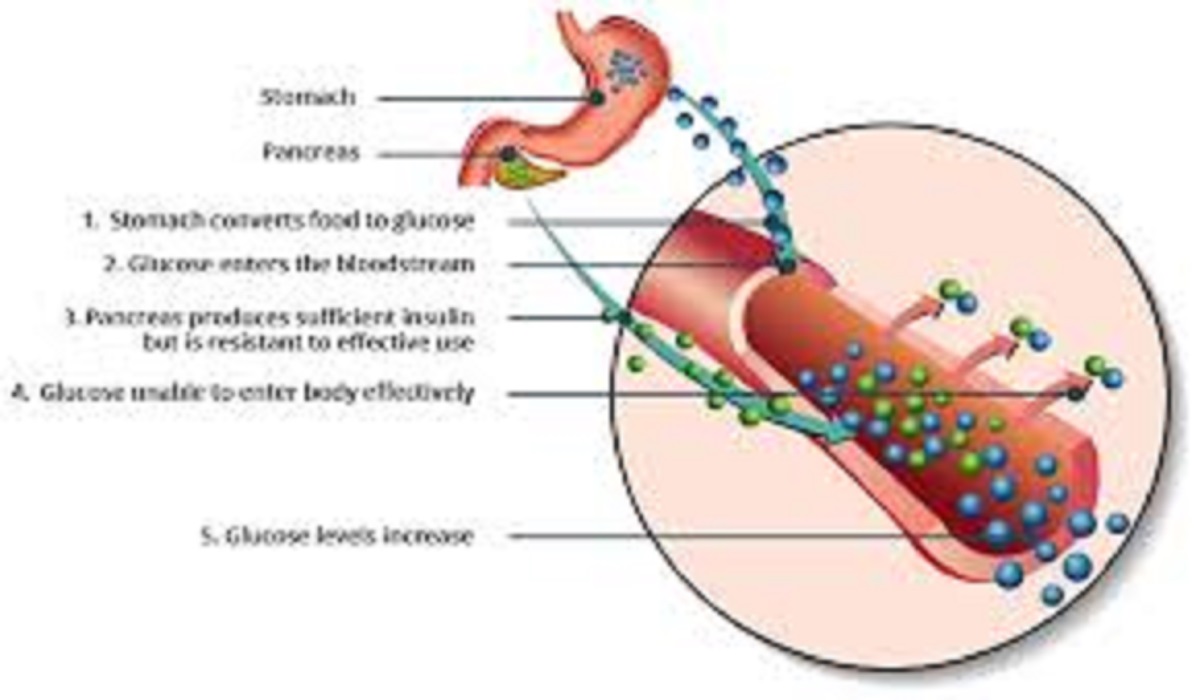
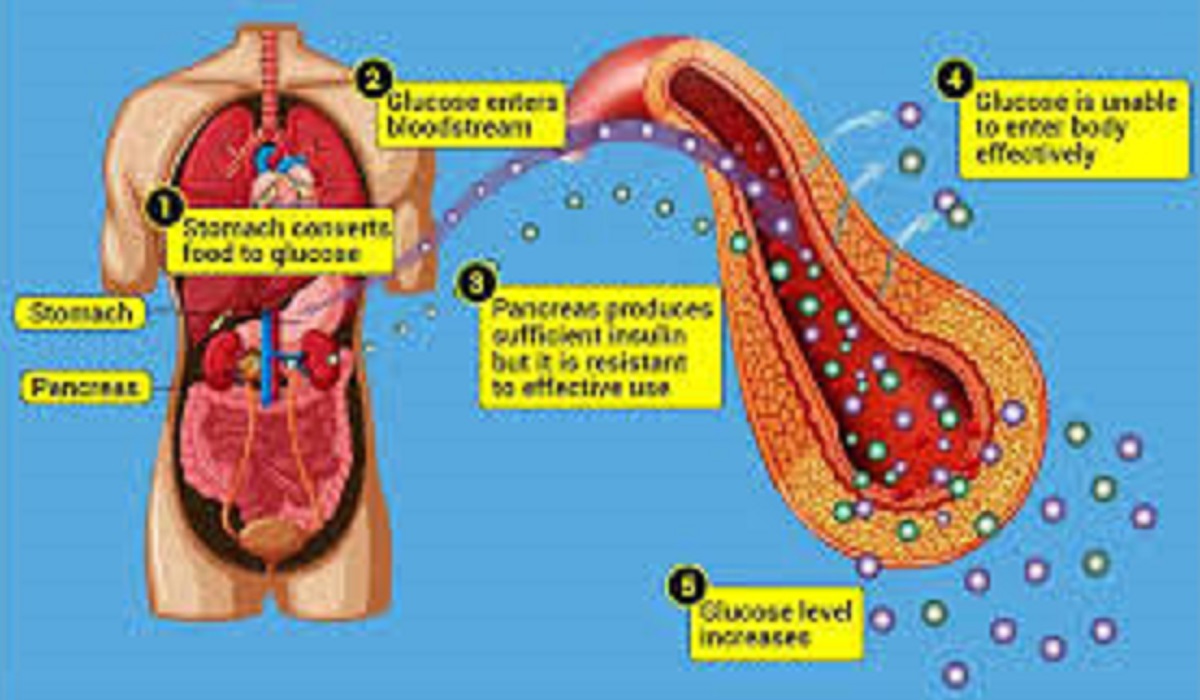
2nd Type of Diabetes & Symptoms: Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder where the body becomes resistant to insulin or fails to produce enough insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels. Unlike Type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune condition, Type 2 is largely influenced by lifestyle factors.
Prevalence and Risk Factors
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), over 462 million people suffer from Type 2 diabetes globally. Key risk factors include:
- Obesity
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Family history of diabetes
- Poor diet (high in sugar and processed foods)
Symptoms of Type 2 Diabetes
Early Warning Signs
- Increased thirst (Polydipsia)
- Frequent urination (Polyuria)
- Fatigue and irritability
Common Symptoms
- Blurred vision
- Slow-healing wounds
- Tingling or numbness in hands/feet (Neuropathy)
Severe Symptoms and Complications
- Heart disease
- Kidney damage (Nephropathy)
- Vision loss (Diabetic retinopathy)
Causes and Risk Factors
Genetic Factors
- Family history increases risk by 40% if one parent has diabetes.
Lifestyle and Dietary Influences
- High sugar intake
- Lack of physical activity
Medical Conditions Linked to Type 2 Diabetes
- PCOS (Polycystic Ovary Syndrome)
- Hypertension (High Blood Pressure)
Diagnosis of Type 2 Diabetes
Blood Tests and Screening
- Fasting Blood Sugar Test (Normal: <100 mg/dL, Diabetes: ≥126 mg/dL)
- Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT)
HbA1c Test Explained
- Measures average blood sugar over 3 months
- Normal: Below 5.7%
- Prediabetes: 5.7%-6.4%
- Diabetes: 6.5% or higher
Treatment Options for Type 2 Diabetes
Lifestyle Changes (Diet & Exercise)
- Low-carb diets (Example: Mediterranean diet)
- 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week
Oral Medications (With Examples)
- Metformin (First-line treatment)
- SGLT2 Inhibitors (e.g., Empagliflozin)
Insulin Therapy (When Needed)
- Long-acting insulin (e.g., Lantus)
- Rapid-acting insulin (e.g., Humalog)
Alternative and Natural Remedies
- Cinnamon supplements
- Berberine (Natural blood sugar regulator)
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Effectively
Blood Sugar Monitoring
- Continuous Glucose Monitors (CGMs)
- Self-testing with glucometers
Importance of Regular Check-ups
- Annual eye exams
- Kidney function tests
Prevention Strategies
Healthy Eating Habits
- Avoid sugary drinks
- Increase fiber intake
Physical Activity Recommendations
- Walking 10,000 steps/day
- Strength training twice a week
Latest Research and Advances (2025-2026)
New Medications
- Tirzepatide (Dual GIP/GLP-1 agonist) – Shown to reduce A1C by 2%
Technological Innovations
- Smart insulin pens
- AI-powered diabetes management apps
Real-Life Examples and Case Studies
Success Story: John’s Diabetes Reversal
- Lost 50 lbs with keto diet & exercise
- Reduced HbA1c from 8.5% to 5.8%
Conclusion
Type 2 diabetes is manageable with the right lifestyle changes, medications, and monitoring. Early detection and proactive care can prevent complications.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. Can Type 2 diabetes be reversed?
Yes, through weight loss, diet changes, and exercise, some people achieve remission.
2. What foods should diabetics avoid?
- Sugary snacks
- White bread, pasta
- Processed meats
3. How often should I check my blood sugar?
- Before meals & 2 hours after eating (If on insulin)
- At least once daily (If on oral meds)
4. Is Type 2 diabetes hereditary?
Genetics play a role, but lifestyle choices are more influential.
5. What’s the latest breakthrough in diabetes treatment?
Tirzepatide (Mounjaro) – A new drug that helps in weight loss and blood sugar control.