What is Diabetes? Symptoms & Treatment
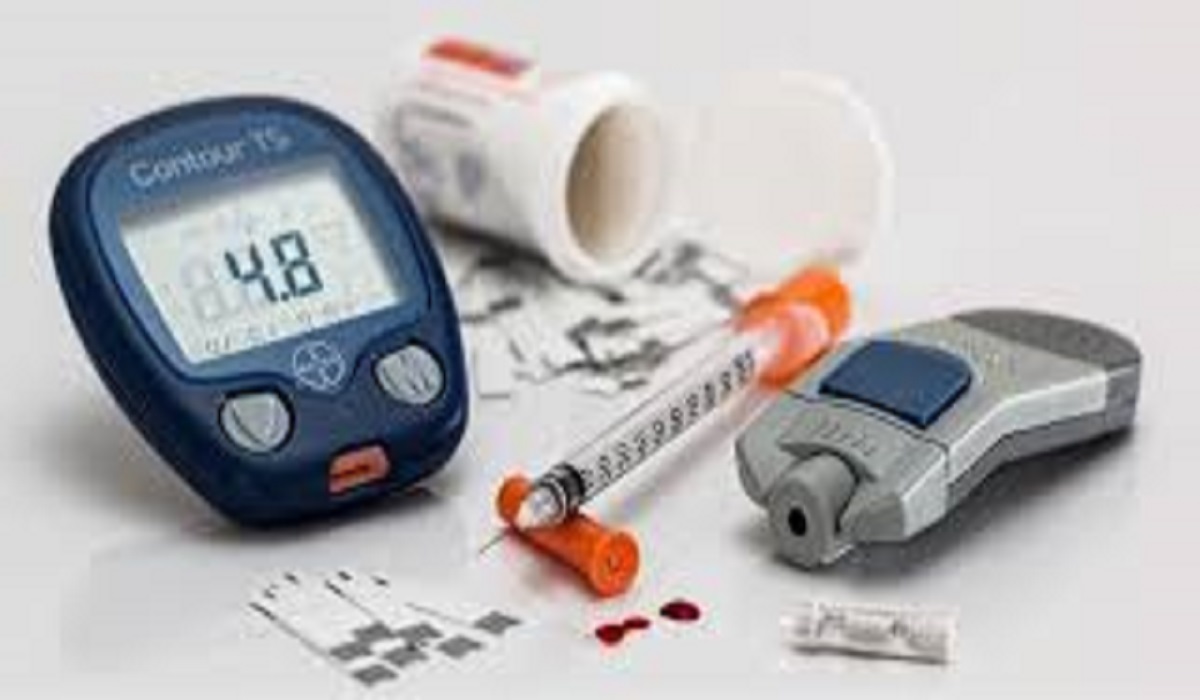
What is Diabetes? Symptoms & Treatment: Diabetes is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by high blood sugar levels due to the body’s inability to produce or effectively use insulin. Insulin is a hormone that regulates blood glucose, allowing cells to utilize it for energy.
Brief History of Diabetes
The term “diabetes” was first recorded in 1500 BCE in Egyptian manuscripts. Later, Greek physician Aretaeus coined the term “diabetes,” meaning “to pass through,” referring to excessive urination. The discovery of insulin in 1921 by Banting and Best revolutionized diabetes treatment.
Global Prevalence of Diabetes
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF), approximately 537 million adults live with diabetes worldwide (2021 data), expected to rise to 643 million by 2030.
Types of Diabetes
Type 1 Diabetes
An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. It usually develops in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 Diabetes
The most common type (90% of cases), where the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough. Linked to obesity, poor diet, and inactivity.
Gestational Diabetes
Occurs during pregnancy due to hormonal changes that cause insulin resistance. It usually resolves after childbirth but increases future Type 2 diabetes risk.
FAQs About Diabetes
1. Can diabetes be cured?
Currently, Type 1 diabetes has no cure, but it can be managed with insulin. Type 2 diabetes can sometimes be reversed with lifestyle changes, weight loss, and medication.
2. What foods should diabetics avoid?
Avoid sugary drinks, refined carbs, trans fats, and excessive processed foods. Focus on whole grains, lean proteins, and fiber-rich foods.
3. How often should I check my blood sugar?
It depends on the type of diabetes and treatment. Type 1 diabetics may need to check 4-10 times daily, while Type 2 diabetics may check less frequently.
4. Can exercise lower blood sugar?
Yes! Physical activity helps muscles absorb glucose, lowering blood sugar levels. Aim for 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
5. Is diabetes hereditary?
Genetics play a role, especially in Type 2 diabetes. If a parent has diabetes, the risk increases, but lifestyle factors are also crucial.
Final Words
Diabetes is a manageable condition with proper care. Early diagnosis, a healthy lifestyle, and medical support can help individuals lead a normal, active life. Stay informed and consult healthcare professionals for personalized advice.